Manufacturing is one of the largest industries in the United States, accounting for approximately 11% of GDP. Almost everything we enjoy on a daily basis – whether it’s the car we drive or the television we play video games on, is made possible because of manufacturing companies.
Due to global competition to produce the highest quality goods, cheaper and faster, manufacturing also tends to be a breeding ground for innovation. This innovation can take many different forms, including cutting-edge robotics, artificial intelligence, and methods for precise machining. As an industry that’s heavily involved in research and development, manufacturing companies are uniquely positioned to take full advantage of R&D tax credits to help offset some of their research costs.
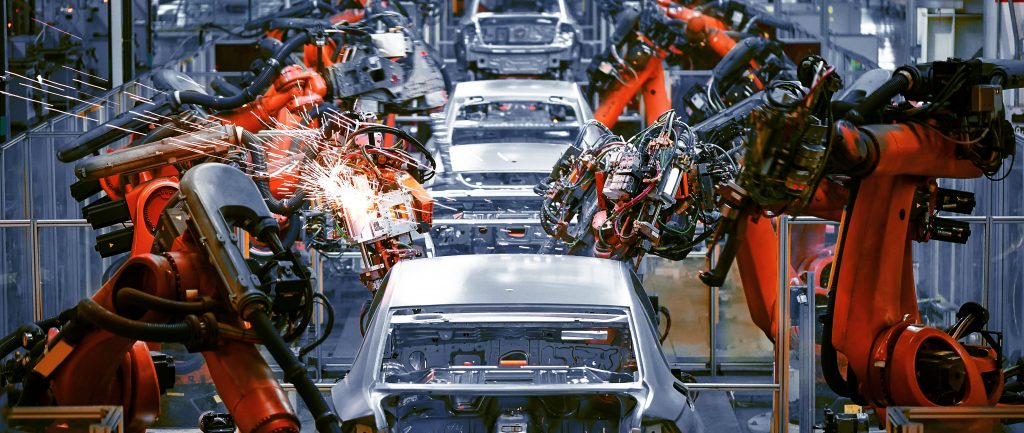

How does a manufacturing company qualify for the credit?
There is a four-part test used to determine whether a company has a project that qualifies for the R&D Tax Credit. If you have a project that meets each of the four quadrants below, your project most likely qualifies.
Technological in nature
- Discover information that fundamentally relies upon principles of Hard Sciences (i.e. Physical Sciences, Biological Sciences, Engineering, Computer Science, etc.)
- Not social, economic, or psychological Permitted Purpose
Permitted Purpose
- Develop a new, or improve an existing, product or process
- Related to Functionality, Performance, Reliability, Quality, Significant cost, Savings, etc.
- Not Aesthetics
Eliminate Uncertainty
- Capability
- Uncertain if able to achieve desired result
- Methodolgy
- Uncertain of optimal design or process to achieve project goals
- Goals to show there were issues and potential alternate solutions
Process of Experimentation
- Evaluate and test alternative design or process to identify optimal solutions
- Methods to use
- Prototyping
- Modeling
- Systematic Process of Trial and Error
- Simulation
- Computer Science Testing (Validation, Beta, etc.)
Once a company determines that their project meets these criteria, three expense categories factor into the tax credit calculation:
Wages
- Employees involved in conducting or carrying out qualified research.
- Employees providing supervision of qualified research.
- Employees providing support for qualified research activities.

Supplies
- Resources consumed or used up during the carrying out of qualified research.

Contract Research
- 3rd parties paid to assist in the conducting or carrying out of qualified research.
- Requires the Company to maintain rights to the project (i.e. research performed on behalf of the Company)
- Requires the Company to bear the expense if the research is unsuccessful.
Manufacturing companies can qualify for the R&D tax credit regardless of the type of production they specialize in. While not all-inclusive, a few examples of manufacturing companies that could claim the tax credit include:

Aerospace
With the rise of big tech and the massive fortunes generated by software companies each year, computer engineering is perhaps the most fast-paced, dynamic industry in the United States. Startups and large software corporations, alike, are in a constant R&D battle to innovate the next big thing or be rendered obsolete. Qualifying R&D activities that a computer engineering company might partake in include:
- Developing new composite materials for commercial jets in order to reduce weight.
- Testing non-military applications for UAVs, such as for farming, law enforcement, or package shipping.
- Designing new aircraft fueled by a biofuel, solar panels, or another renewable energy source.
- Developing specialized tooling to automate part of a production process.
- Upgrading or refining aircraft software used for navigation or communication.
- Designing a specialized part for use by a larger aerospace manufacturer, like Airbus or Lockheed Martin.
As aircraft designs are constantly evolving to meet the demands of a society who wants to travel cheaper, faster, and with less of an environmental impact, R&D will always be a key aspect of the aerospace industry.
Chemical
The chemical industry is responsible for taking raw materials that can be found in nature, such as metals, minerals, and oil, and converting them into a form that can be utilized in some way by society. Without the chemical industry, most manufacturing processes in other industries would be impossible. Chemical manufacturers spend large amounts of money on R&D in order to improve the production process for the chemicals that they produce, as well as working to develop new chemicals and chemical applications. A few examples of qualifying R&D activities include:

- Developing new or improved chemicals to be used within the manufacturing industry.
- Creating new polymers which can be more-easily recycled.
- Designing materials to withstand extreme environments, such as those encountered in the aerospace industry.
- Developing equipment to process raw materials, such as oil or gas, more efficiently.
- Developing a new type of perfume, pesticide, toothpaste, cleaning product, or other chemical product available for purchase by the general consumer.
The opportunities are endless – whether your company designs space shuttles or sewer pipelines, you are likely eligible to take advantage of the R&D Tax Credit.
Firearms and Ammunition
Firearms and ammunition manufacturers design, build, and test weapons for the military, law enforcement, and recreational gun owners. These manufacturing companies conduct R&D to improve the accuracy, rate of fire, comfort, and safety of their weapons and ammunition while cutting the production time and cost. Qualifying R&D activities regularly performed in this manufacturing sector include:
- Improving the optics on a scope with new materials or hardware to increase the accuracy
- Developing new microstamping technologies to help locate criminals after a weapon has been used for a crime.
- Designing or testing gun safety technologies which require the owner to verify their identity before the weapon can be fired (e.g. through fingerprint or voice).
- Designing or implementing new manufacturing equipment which improves a process through automation.
- Development of new training tools such as lasers, software tracking, etc. in order to facilitate improved performance for the user.
Even if a manufacturer isn’t necessarily working to improve their current weapon design, they are likely involved in R&D to reduce their production costs and increase throughput which often qualify under the R&D Tax Credit.
Medical Equipment
Never has the need for a steady supply of medical equipment been so apparent than with the Covid-19 pandemic. Seemingly overnight, companies who manufacture necessary medical supplies like ventilators, examination gloves, and masks were forced to kick production into overdrive. Many manufacturers in non-medical industries have recently pivoted their production to help meet the high demand for certain medical products such as PPE decontamination units. Before the pandemic, R&D within the medical manufacturing industry was still very important – as health issues are constantly evolving, companies must also quickly evolve to stay ahead of the curve. A few examples of qualifying R&D activities within the medical equipment manufacturing industry include:
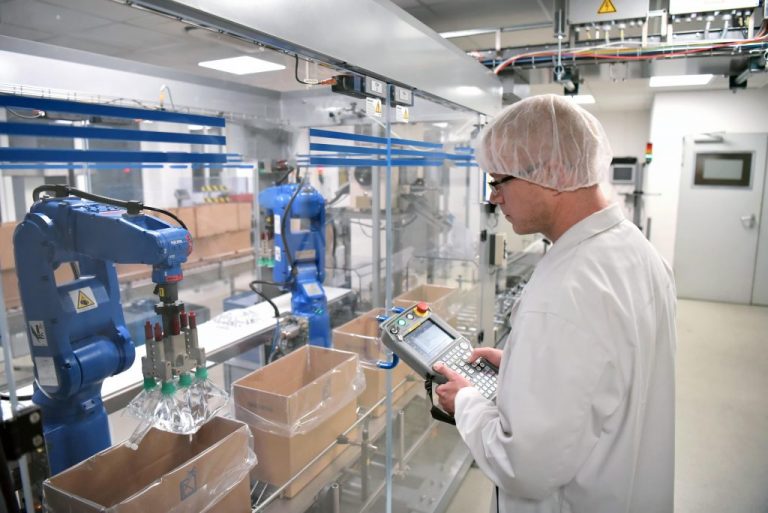

- Performing CAD modeling or developing drawings for a new medical device,
- Developing new products or designing features for an existing product.
- Implementing automation/robotics to improve efficiency of manufacturing process.
- Developing a new packaging process to increase speed or sterility of the medical product.
- Designing and conducting testing programs to satisfy regulatory requirements (e.g. for FDA approval).
- Developing and testing a new software to integrate into the manufacturing process for quality control, safety, efficiency, etc.
- Developing and testing new software to integrate into a medical device, like a pacemaker.
As structural engineering is largely trial and error during the design process, almost every structural engineering project has a strong case for claiming the R&D Tax Credit.

Job Shops
Job shops conduct specialized manufacturing, where instead of churning out identical products 24/7 on an assembly line, they receive drawings, specifications, or other instructions for a given system or product and work to provide a final manufactured product that meets these requirements. Sometimes this may involve a single component while in other situations a customer may require a batch of a given component. There are many tasks regularly performed by job shops which qualify as R&D. Some of these qualifying activities include:
- Programming CNC machines or creating cut files for a mechanical component
- Designing components using CAD to develop drawings
- Performing finite element analysis or other modeling based on CAD models
- Evaluating alternative materials to be used on a given project to optimize strength, durability, or cost savings
- Developing new process flows to improve efficiency
- Implementing robotics to automate certain processes.
Job shops can increase the quality of their products, cut production costs, and increase throughput by developing new, innovative ways to conduct business. Many of these activities qualify for R&D Tax Credits, which provide an additional incentive to conducting the research.
Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding is a manufacturing process that involves injecting molten materials, most often a thermosetting polymer, into a mold. Once the melted polymer cools, it hardens to form the shape of the mold and is subsequently removed. Due to the widespread application of plastics, this technology is used in many different industries. With the rise of 3D printing technologies, the plastics industry in general has become a very hot industry for R&D. 3D printing makes it possible to create plastic forms without the need to create a metallic mold, which provides flexibility and reduced cost for specialized plastic forms. Many activities in the plastics industry qualify as R&D. Some of these activities include:
- Designing and fabricating molds to be used to create a given plastic product.
- Modeling plastic molds in autoCAD or SolidWorks software.
- Experimenting with new polymers to inject into the molds.
- Integrating 3D printing technologies into the production facility for specialized forms.
- Automating certain manufacturing processes with robotics.
- Optimizing the production process by testing different temperatures, pressures, or other conditions that factor into the final product.
- Using structural modeling programs to test the integrity of injection molded products.
Whether your company is working to optimize your existing injection molding process or integrating new technologies like 3D printing into your operation for specialized tasks, many of the costs incurred to perform this R&D qualify for tax credits.

Tool & Die
Tool and die manufacturers focus on making the tools used for manufacturing in separate industries, such as automobiles, aerospace, plastic injection molding, etc. They design and create molds, dies, jigs, fixtures, and other tools which can be used by machinists and engineers to increase the efficiency and safety of their manufacturing process. As toolmakers must constantly innovate and problem solve to meet their clients’ individual production needs, they often partake in qualifying R&D activities, the cost of which can be offset by the R&D Tax Credit. Some of these activities include:
- Improving an internal production process through the implementation of new technology (e.g. 3D printing).
- Modeling components in a software such as autoCAD or SolidWorks prior to beginning fabrication.
- Experimenting with new materials to improve the strength and durability of the tools being manufactured,
- Developing an improved design for a mold, die, jig, or fixture.
- Developing or testing a new hardware or software to help streamline the production process
Tool and die companies must conduct R&D in order to support manufacturers in fast-paced industries where the technology is constantly changing. If your manufacturing company is involved in toolmaking, there is a good chance you’re performing qualifying R&D activities without even knowing it. These tax advantages could help your company realize significant tax savings, allowing you to continue investing R&D to support your clients to the greatest extent possible.
Metals
Companies who manufacture metals are responsible for processing raw materials, such as iron ore, into a form like hot-rolled steel that can be utilized by manufacturers. This involves complex chemical processes and specialized equipment, as well as controlling many different variables that factor into the overall quality of the end product. Metallurgy is an entire field within materials engineering which takes part in large amounts of R&D to constantly develop better metals. A few qualifying R&D tasks that are common to the metals manufacturing industry include, but are certainly not limited to:

- Developing a new heat treatment process for refining metals
- Improving part of the forming process (hot or cold forming).
- Designing new tools to improve the production process.
- Using emerging technologies, such as robotics, to automate certain production processes.
- Conducting metallurgical research to develop new types of metals, or improving the end product of the existing metal.
- Developing and testing a new internal process to improve quality control or safety.
- Researching new ways to reuse or recycle scrap metal from the production process.
- Conducting structural analysis on metal products to improve the strength and durability properties.
If you work in the metals industry and are involved with developing new processes or technology to improve your production process, you likely qualify for significant yearly tax savings that can be realized through R&D Tax Credits.

Oil & Gas
Oil and gas companies are responsible for extracting crude oil from the earth, then refining this crude oil into petroleum products that quite literally keep our society running. Typically, oil extraction and oil refinery are separate parts of the supply chain and are performed by separate companies. The oil refinery process is much like chemical and metal processing, where raw materials are converted into a composition that can be used by society to power our cars, make our airplanes fly, and many other important things. As oil and gas manufacturers continue to receive environmental pressure to move towards more green operations, R&D has never been more important in the industry. A few qualifying R&D activities include:
- Developing new methods or processes to extract, transport, or refine crude oil more efficiently.
- Improving drill designs to increase capacity and/or efficiency of oil rigs.
- Conducting environmental testing to mitigate byproducts which are harmful to the environment.
- Using modeling or CAD technologies in the design of a piece of equipment, or an entire plant.
- Testing fuel combustion to optimize efficiency.
- Testing fuel Developing new technologies or software to aid in oil exploration.to optimize efficiency.
The oil and gas industry will continue to face significant challenges in the coming decades, and companies will be required to innovate to survive in the cutthroat environment. R&D will continue to be a key aspect of the oil and gas business, and R&D Tax Credits can help companies realize significant savings.
Claim your R&D Tax Credits Today
Whether you own a small business, work for a large corporation, or fall somewhere in between – if your company operates within the engineering industry there is a good chance that your projects qualify for R&D Tax Credits. LEAF Specialty Tax Consultants focus exclusively on helping companies like yours take advantage of R&D Tax Credits allowing you to continue to innovate while maximizing your profitability. If you’d like to begin the conversation and find out more about how we can help your company innovate and grow, contact us today!

